Solution Strategy
Chosen Architecture
Layered Architecture
This document processing application utilizes a layered architecture approach to achieve modularity, maintainability, and separation of concerns. While other architectures offer advantages for complex applications, a layered architecture provides a simpler and potentially more efficient solution for this specific use case.
Here's a breakdown of the key layers within this chosen architecture:
Presentation Layer
This layer handles user interaction and presentation logic. It utilizes the frontend framework (Nuxt.js with Tailwind CSS) to build the user interface for uploading documents, giving it metadata, grading the documents, viewing the documents, distributing the documents, and downloading documents.
The frontend communicates with the backend API (FastAPI) through well-defined endpoints to initiate document upload, tagging, and authorization.
This layer focuses on providing a user-friendly experience for interacting with the application.
Business Logic Layer
This layer houses the core application logic for document uploads, storage, and retrieval. It resides within the FastAPI backend application.
Responsibilities include:
- Receiving document uploads from the presentation layer.
- Validating uploaded documents (e.g., file type, size).
- Queue uploads with a message broker (RabbitMQ).
- Handle distributed task queues (Celery).
- Watermark, preview, and download of documents.
- Provide authentication, authorization, and access control to documents.
- Caching (Redis).
- Interacting with the data access layer to store and retrieve documents and their metadata in order to approve, preview, rate, download, or distribute data.
This layer encapsulates the business rules and logic for handling document uploads, storage, and retrieval.
Data Access Layer
This layer abstracts the interaction with the underlying database management system (PostgreSQL database).
It utilizes an ORM (Object-Relational Mapper, SQLAlchemy) or a database access library to interact with the PostgreSQL database securely.
Responsibilities include:
- Storing documents (in Azure Blob) and their associated metadata in the relevant tables (upload timestamps, processing status).
- Retrieving relevant data based on requests from the business logic layer.
- This layer shields the business logic from the specifics of the database implementation, promoting code reusability and maintainability.
Benefits of Layered Architecture:
Modular Design: Clear separation of concerns between presentation, business logic, and data access layers promotes maintainability and easier testing.
Scalability: The architecture can be scaled by adding resources to individual layers as needed (e.g., scaling the database server for increased data storage).
Simpler Implementation: Compared to a most of the other architectures, a layered architecture can be easier to set up and manage, particularly for smaller or less complex applications.
Technology Stack
We'll leverage a Python and Javascript technology stack to achieve our goals:
Backend:
FastAPI:
- This high-performance framework is ideal for building the application's RESTful API, enabling efficient handling of document uploading, storage, and retrieval.
Celery:
- Asynchronous task processing with Celery is crucial for handling document tasks efficiently. This ensures responsiveness by offloading tasks from the main thread.
Redis:
- A fast in-memory data store like Redis is well-suited for caching frequently used data (e.g., pre-processed entity recognition models) and storing temporary results during document operations improving overall performance.
PostgreSQL:
- This robust object-relational database (ORDB) provides a secure and reliable storage solution for:
- User information (if applicable for authentication and authorization).
- Document metadata (e.g., upload timestamps, processing status).
Frontend:
Nuxt.js:
- Nuxt.js remains one of the foundational choices for building a user-friendly frontend application.
- Nuxt.js is better suited than Vue.js due to it not being a single-page application, thus it allows us to add SEO (Google Analytics) tags on a more granular manner.
- It provides a streamlined development experience with opinionated features like routing, server-side rendering, and automatic code-splitting.
- This will help multiple team members adhere to a structure that is predetermined and opinionated.
Tailwind CSS:
- This utility-first CSS framework allows for rapid development of responsive user interfaces. Tailwind's pre-built classes eliminate the need for extensive custom CSS, saving development time and promoting code maintainability. Features like themes, tree-shaking, and intellisense adds to a much better experience for developers.
Pinia:
- This lightweight state management library for Vue.js is the defacto state library as per the official documentation of Vue.js. Pinia allows you to manage application state in a modular way, simplifying data management for tasks like API data and tracking user actions.
Azure Cloud Services Configuration:
Azure Database for PostgreSQL:
To ensure robust data storage and retrieval, Azure Database for PostgreSQL is selected, it is also Open-Source and free. This managed service provides scalability, security, and reliability for storing sensitive information such as user data and document metadata. It also has various extensions, created by the community, to extend functionality.
Azure Container Apps:
Azure Container Apps is a server-less platform that allows you to maintain less infrastructure and save costs while running containerized applications. Azure Container Apps allows us to create application multiple environments where components within the application environment can talk to each other via localhost and can communicate to other application environments via HTTP and GRPC all within the same network.
Azure Containers:
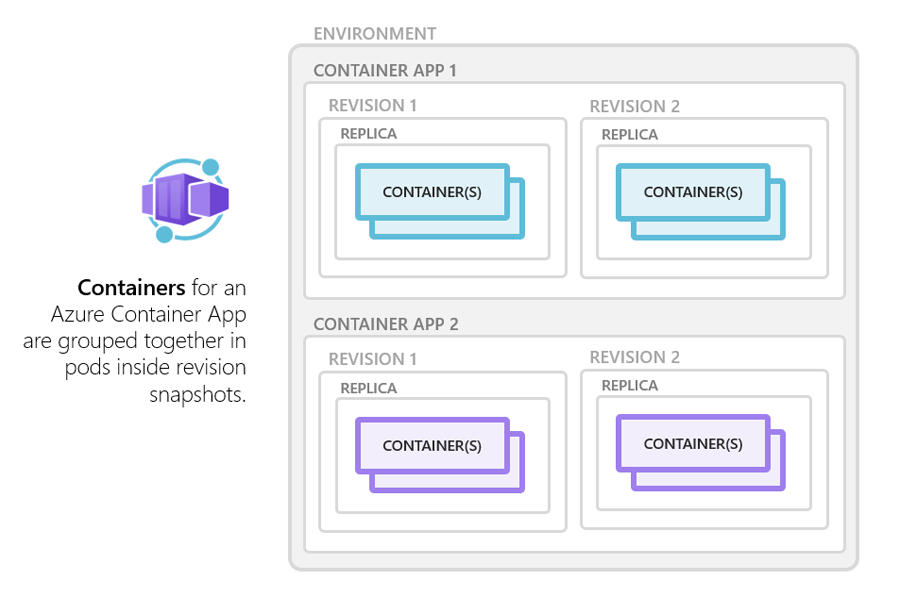
Azure Container Apps Example:
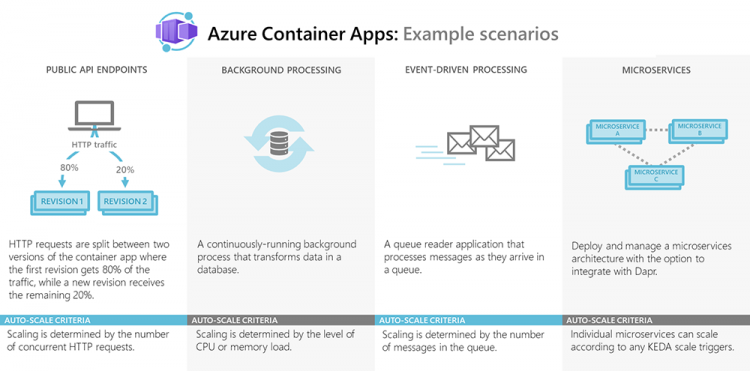
Azure Container Apps using Dapr:
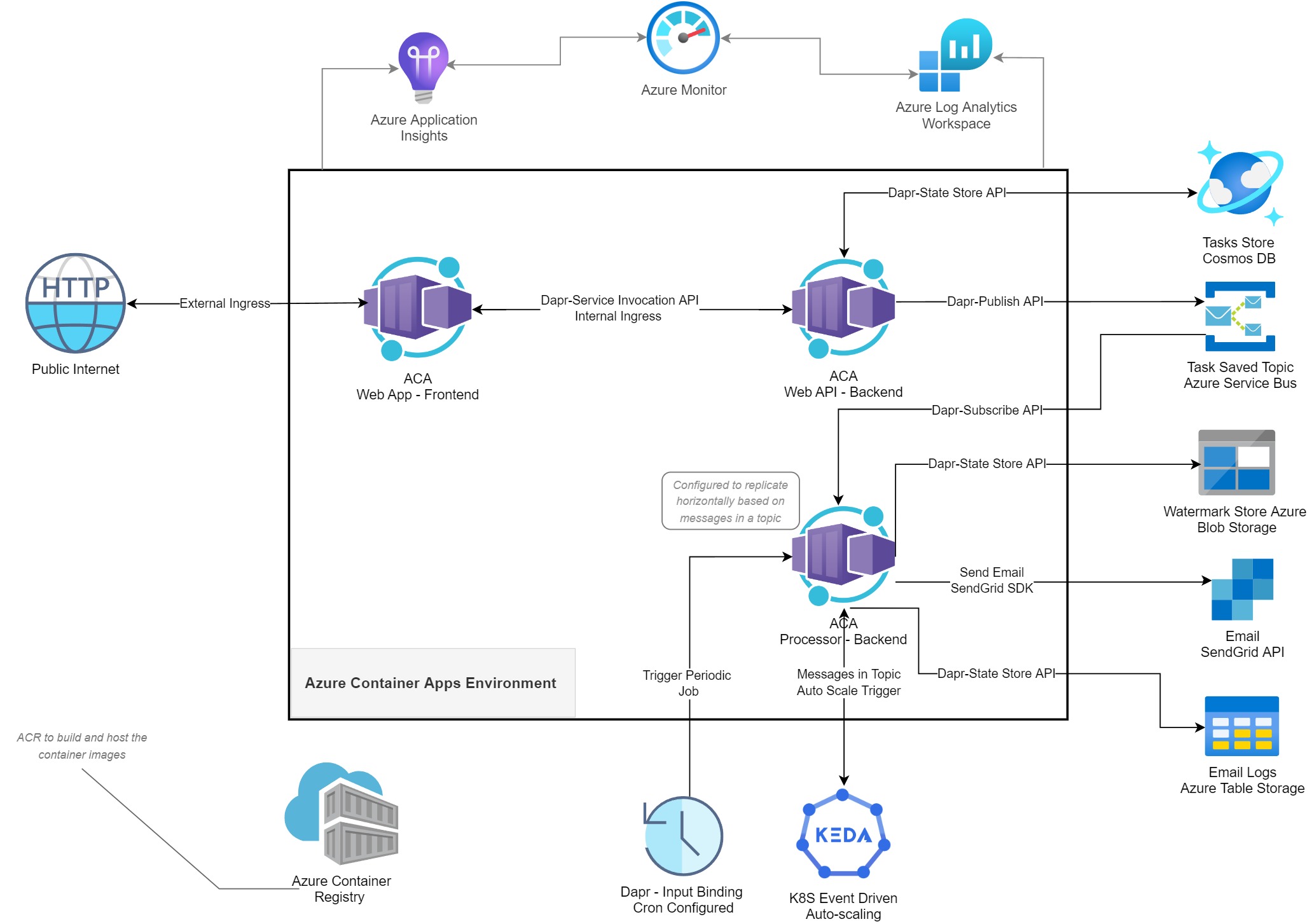
Future Considerations:
In the future, should the need arise for one of the layers of the layers architecture to be scaled individually, separate from the others, we will be able to do so. Also, Azure Container Apps allows us to scale down to zero and scale up to n-amount, should the need arise. Azure Container Apps abstracts away a lot of the complexities of orchestration tools like Kubeternetes, which might be necessary for more complex applications, but not for this specific application.
In the future, if we want to build out additional micro-services, we can modularly intergrate with it, or serve it as a stand-alone service. We can also use this to monitor our containers individually, or as a whole. Azure Container Apps provides intergrated security services at scale.